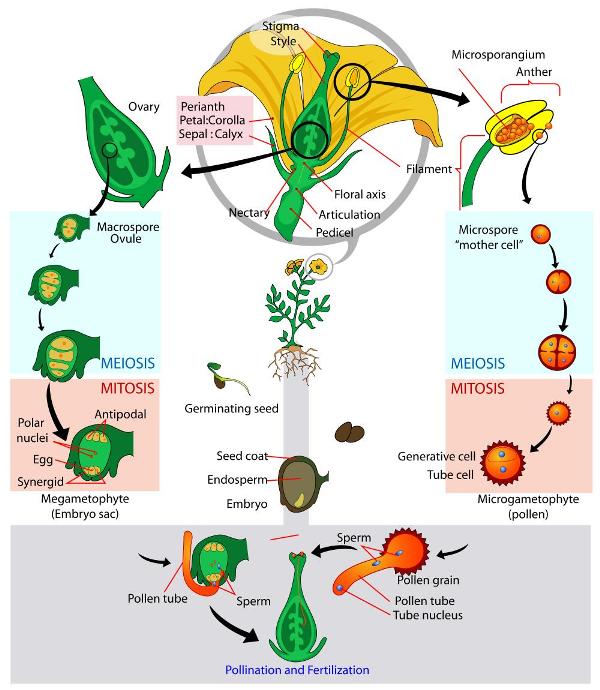
· Most plants grow from seeds These seed plants fall into two groups, angiosperms and gymnosperms Angiosperms are the flowering plants Their seeds develop inside a female reproductive part of the flower, called the ovary, which usually ripens into a protective FRUITGymnosperms (conifers, Ginkgo, and cycads) do not have flowers or ovariesOr what methods do they adopt for reproduction? · The fossil plant Elkinsia polymorpha, a "seed fern" from the Devonian period—about 400 million years ago—is considered the earliest seed plant known to date Seed ferns ( (Figure) ) produced their seeds along their branches, in structures called cupules that enclosed and protected the ovule—the female gametophyte and associated tissues—which develops into a seed

Ovary Botany Definition Structure Britannica
Seed dispersal reproduction in plants
Seed dispersal reproduction in plants-Plant species use different ways to reproduce Millions of years ago early plants reproduced by making spores Ferns still use this method today More modern plants make seeds and flowers Others reproduce by cloning These plants grow new plants from the stems, roots, or leaves of a single parent plant 6 More than 300,000 plants live on EarthA seed is a mature ovule typical of gymnosperms and angiosperms plants commonly called flowering and nonflowering plants from which a new plant grows With seeds, all plants, considered spermatophytes, are spread and propagated Inside the seed, there is the embryo from which the new plant will come out if all the right conditions are met
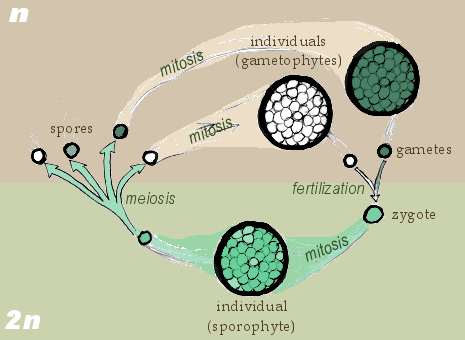


Plant Reproduction Organismal Biology
Seed plants appeared about one million years ago, during the Carboniferous period Two major innovations—seed and pollen—allowed seed plants to reproduce in the absence of water The gametophytes of seed plants shrank, while the sporophytes became prominent structures and the diploid stage became the longest phase of the lifecycleHow Do Plants Reproduce Reproduction of Corn The fertilized ovule will become one of the seeds of the tomato fruit The seed contains the embryo and the endosperm and is covered by a strong seed coat, called the testa The testa is unique to tomatoes The seed forms a thick outer epidermal layer · This special issue focuses on diverse aspects of plant reproduction, including apomixis and sexual plant reproduction, germline identity, plant domestication, and fruit ripening From the moment that a plant switches from vegetative to reproductive growth through to when a seed is finally formed, an intricate network of signalling and regulatory pathways are activated
Some winddispersed seeds could fall in water or on stones, for example2113 · Blog April 7, 21 3 screen shares for 3 different teaching scenarios; · Seed Plants Emerge An ovule is a female reproductive structure in seed plants that contains a tiny female gametophyte The gametophyte A grain of pollen is a tiny male gametophyte enclosed in a tough capsule (see Figure below ) It carries sperm to an Windblown pollen might land anywhere and
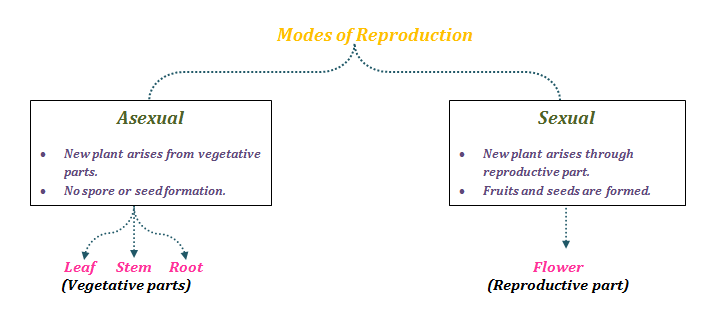
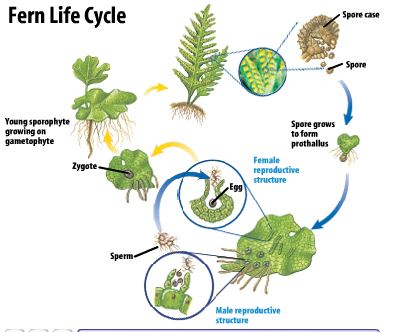
· In most plants, the seedlings are developed from their seeds, which is obtained from flower when the male and female parts of flower meet to form union, seeds are obtained from flower Asexual or Vegetative Reproduction the use of vegetative parts of plants (leaves, stems, buds and roots)Sexual reproduction results in offspring genetically different from the parents Asexual offspring are genetically identical New individuals may be packaged in a protective seed, which can be long lived and can disperse the offspring some distance from the parent In flowering plants, the seed is contained inside a fruit, which protects theSeeds and Flowers Plant reproduction Plants without seeds ☼ Use Spores for reproduction 1 All Nonvascular plants E g Phylum Hepatophyta (Liverworts) Phylum Anthocerophyta (Hornworts) Phylum Bryophyta (Mosses) Plants without seeds 2 Phylum Pterophyta (Ferns) (spores in sporangia on underside of fronds) 3
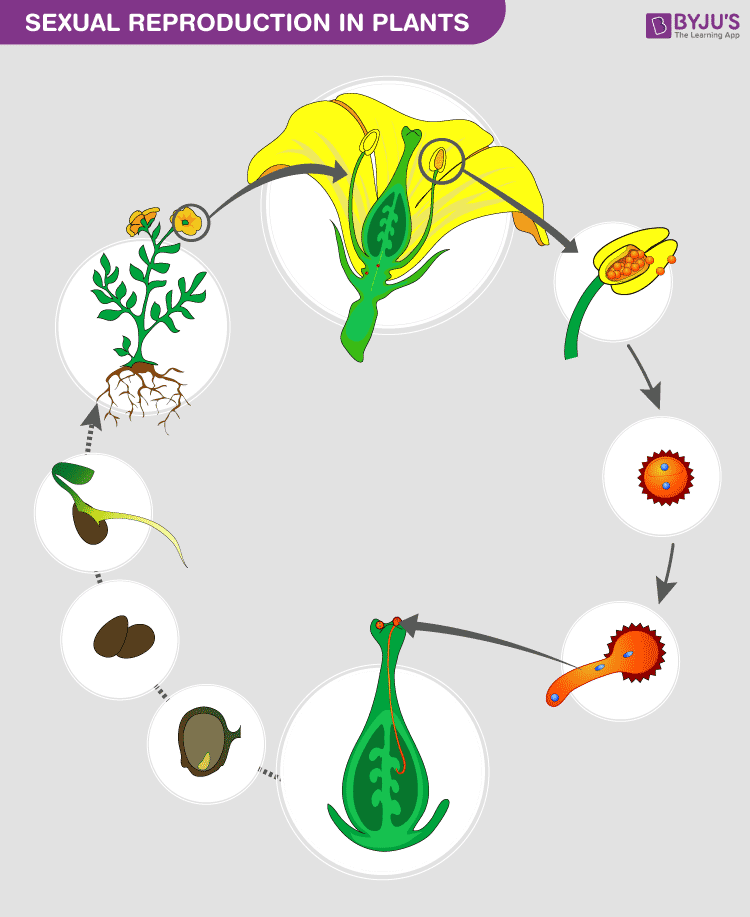


Sexual Reproduction In Plants Features And Its Process



Plant Reproduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
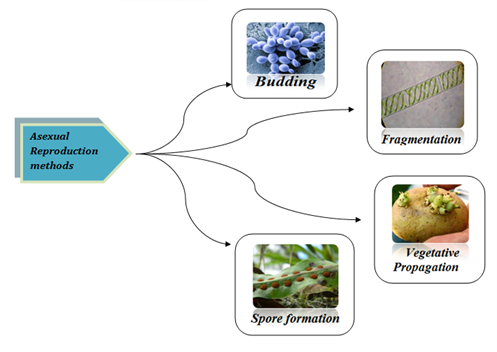
1701 · The parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the parent plant that fall to the ground For example, animals or the wind can break stems or leaves off plants This is one of the ways that plants like liverworts and mosses reproduce · Seed plants produce the spores via sexual reproduction They require bees and/or male and female plants to make them bloom and create seedsSpore formation Vegetative Propagation Most plants have roots, stems and leaves


Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs



Understanding Students Conceptions Of Plant Reproduction To Better Teach Plant Biology In Schools Lampert 19 Plants People Planet Wiley Online Library
· In addition, reproductive efficiency in seed plants is largely influenced by life form and breeding system (Sutherland and Delph, 1986, Sutherland, 1986, Ramírez, 1993) lifeform is intimately related to photosynthetic pathway (Medina, 1995, Ehleringer, 1995, Wang, 05) and succulence is closely related to CAM species (McWilliams, 19700211 · The mode of reproduction decided the genetic structure of the plant Asexual reproduction produces new organisms without seeds while in sexual reproduction, seeds are mandatory This is just one of the differences They have several methods and processes under them Let's look at Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Plants in detailThe phenomenon of Seed Dispersal helps in reproduction in plants But what ex Ever wondered how seeds from one Plant get sown in a different area altogether?
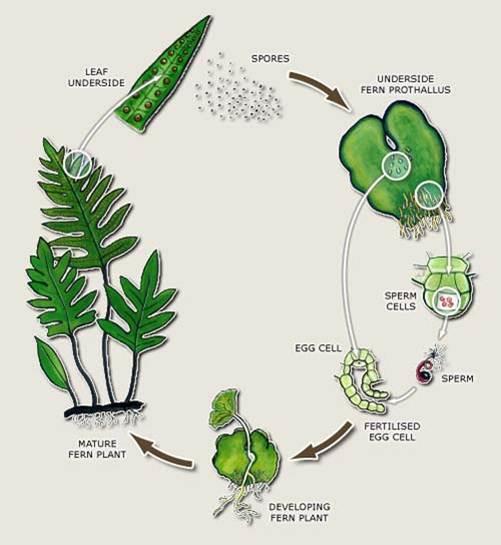


Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic
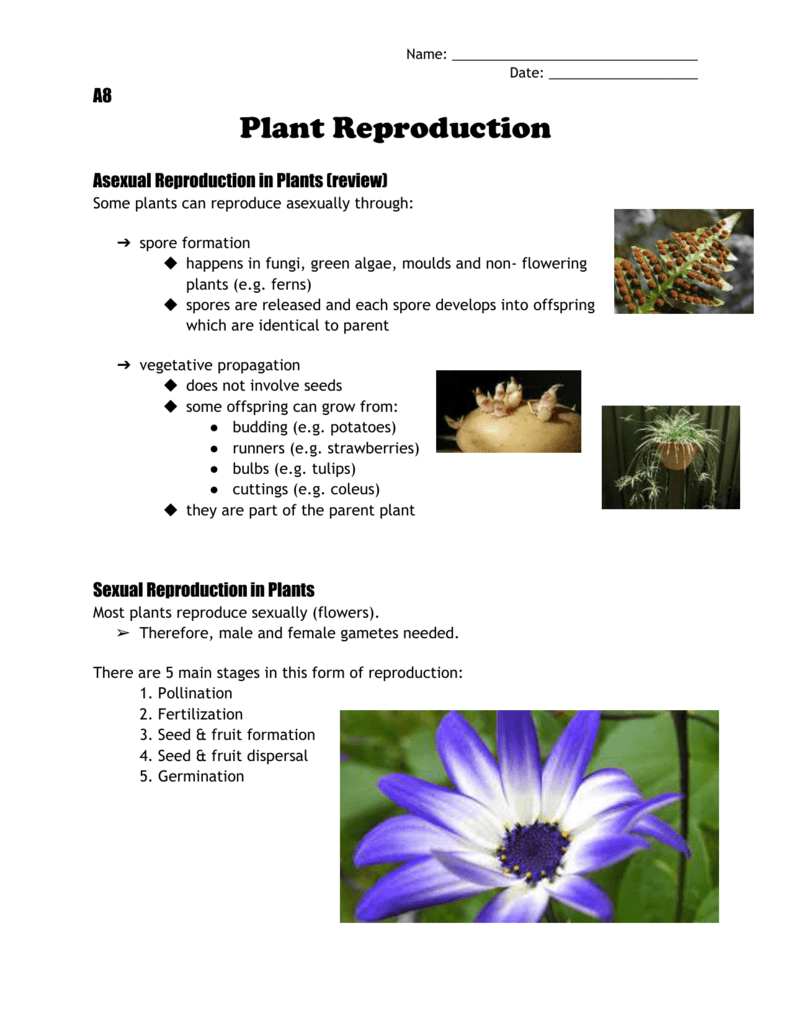


12 Plant Reproduction
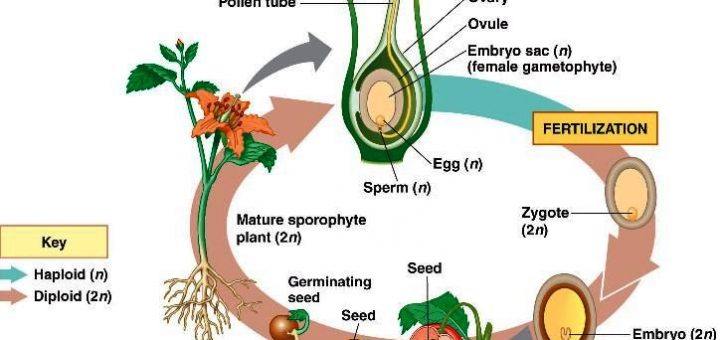
Title = "Sexual reproduction in seed plants, ferns and mosses", abstract = "Behandeling van de biologie met betrekking tot de geslachtelijke voortplanting van deze plantesoort en onderzoek en vermeerderingstechnieken op dit gebiedOF SEEDS AND OTHER PLANT REPRODUCTIVE PROPAGATING MATERIAL Since 1 February , the United Kingdom has withdrawn from the European Union and has become a "third country"1 The Withdrawal Agreement2 provides for a transition period ending on 31 December 3 Until that date, EU law in its entirety applies to and in the United Kingdom4 · When a pollen grain lands on the stigma of a flower of the correct species, a pollen tube begins to grow It grows through the style until it



Reported Temperature Negative Effects On Reproduction Output In Plants Download Table



Fun Germination Facts For Kids
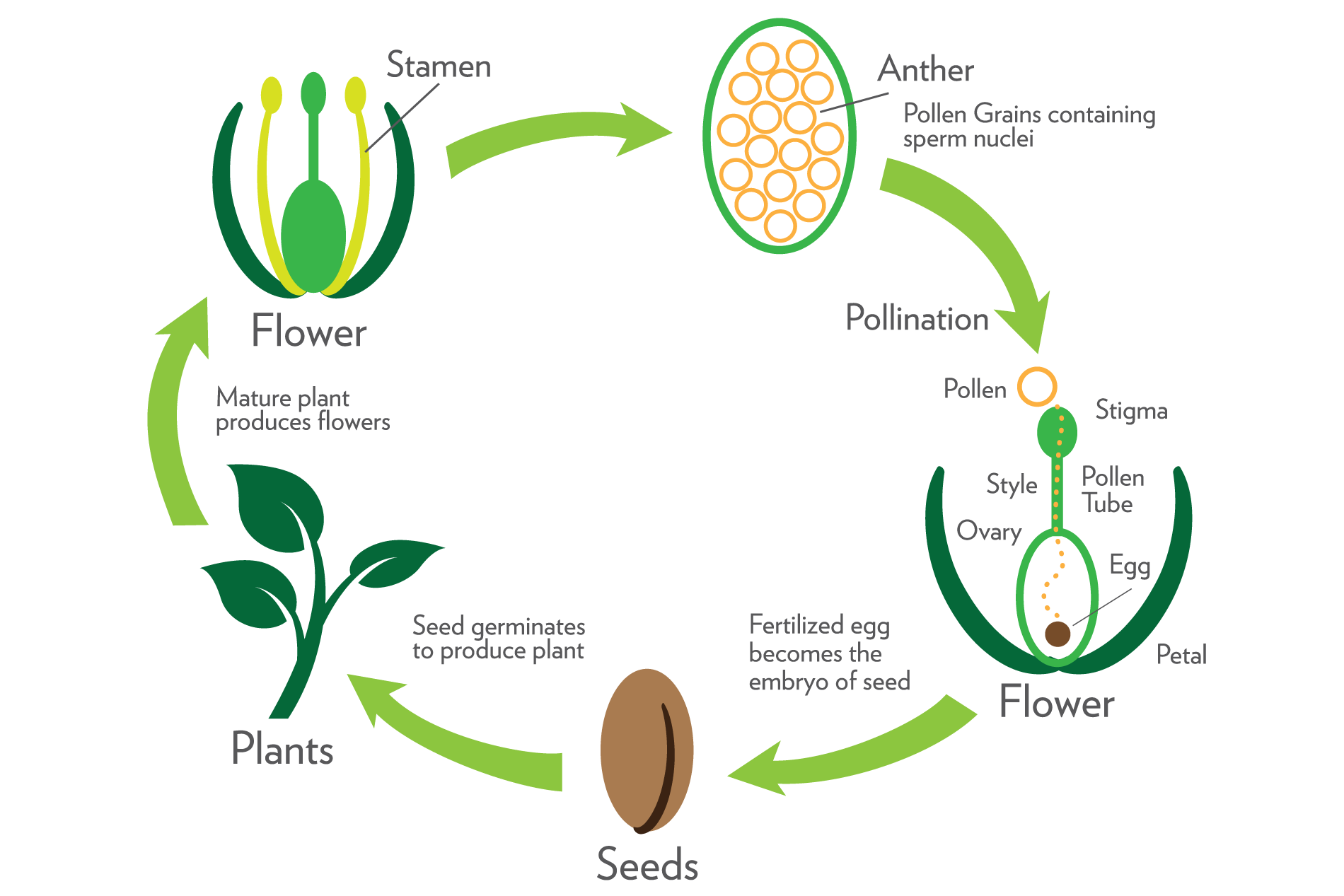
The switch to flowering is a response to the length of light and dark periods in many plants Success in plant reproduction depends on pollination, fertilization and seed dispersal Most flowering plants use mutualistic relationships with pollinators in sexual reproduction Applications andThe video explains how plants reproduce through seeds It shows how seeds germinate and what are required for germination It also explains the importance of · In sexual reproduction, a fusion of male and female gametes produces fruits that contain seeds The seeds give rise to new plants A flower is the reproductive part of a plant which can either be unisexual or bisexual Stamen is the male reproductive part and pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower



Seed Dispersal Interactive Worksheet



Seed Plant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
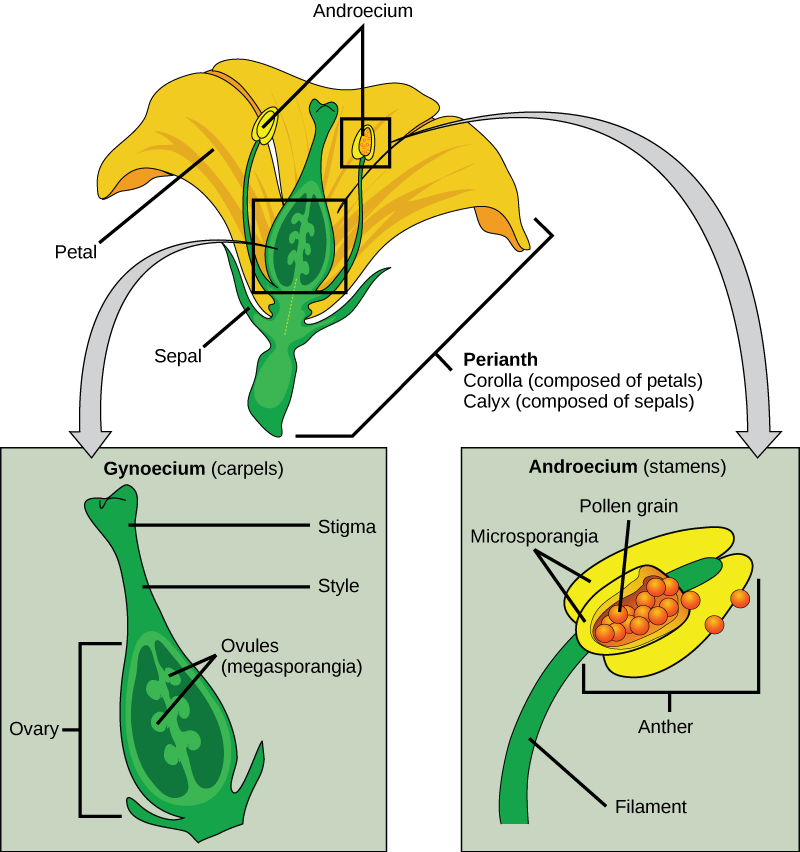
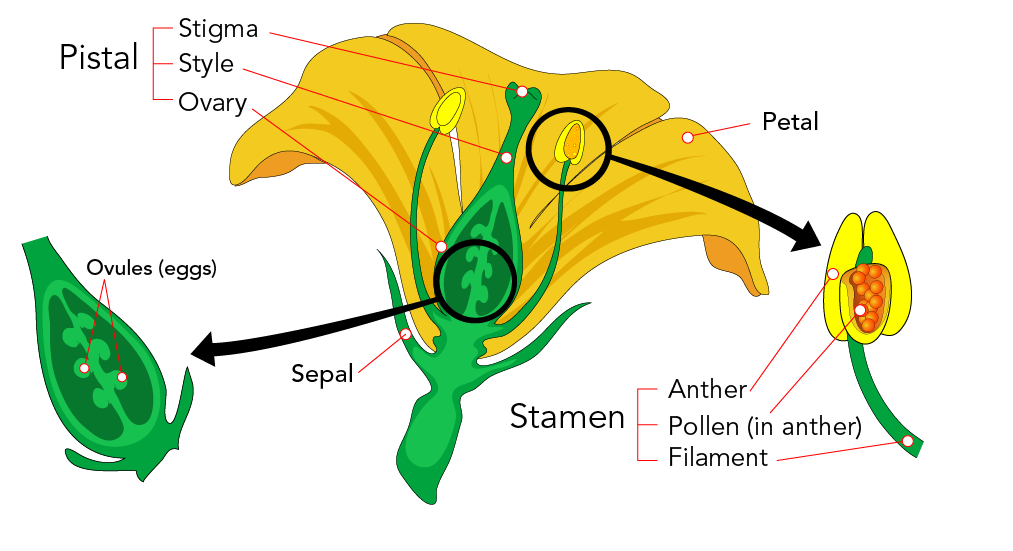
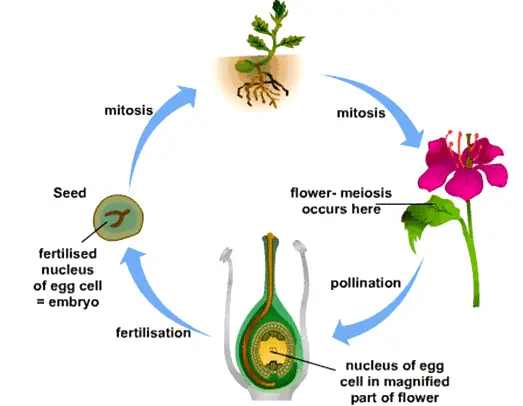
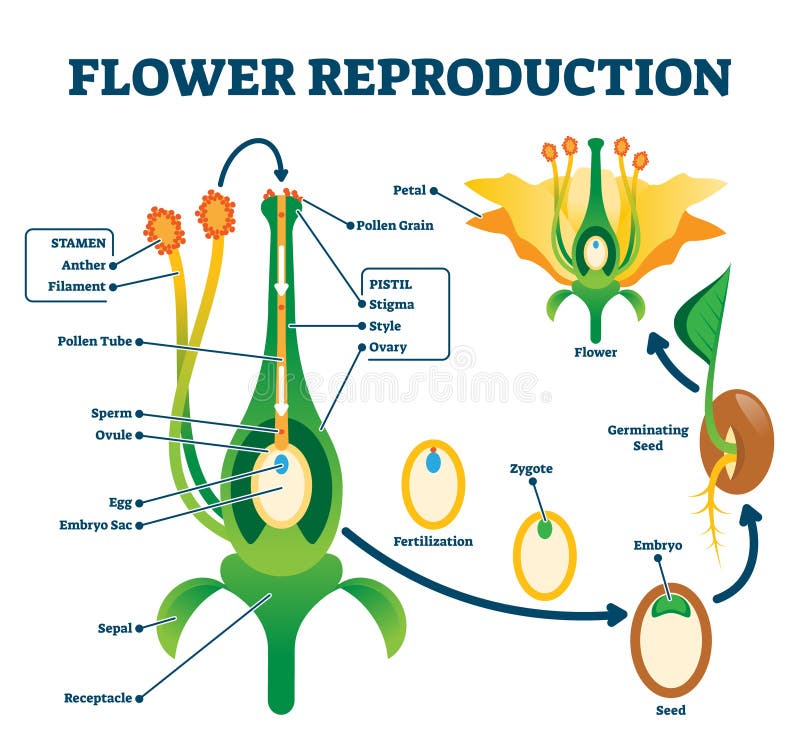
· Sexual reproduction in plants The flower is the reproductive organ of the plant It usually contains male organs (pollen containing pollen containing sperm) and female organs (an ovary containing eggs, from which leaves a leaf and a scar in the head) After fertilization, ovulation with the eggs develops into fruit with seeds · Seed A seed is a part of a flowering plant involved in reproduction It consists of three major parts the embryo, endosperm, and testa The embryo is produced when male and female elements are combined during reproduction It will eventually grow into a new plant2603 · The reproduction happens by different processes that occur in plants and give rise to a descendant plant Fruits and seeds are the results of sexual reproduction The seeds further contribute to the growth of a new plant Process of Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction of plants happens in flowers Flowers produce both female and male



Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download



Plant Propagation Wikipedia
Seed Germination Plants produce many fruits and therefore many seeds This is because only a few of these seeds will find suitable places and conditions in which to germinate The majority of the seeds will be wasted;The evolution of seeds allowed plants to decrease their dependency upon water for reproduction Seeds contain an embryo that can remain dormant until conditions are favorable when it grows into a diploid sporophyte Seeds are transported by the wind, water, or by animals to encourage reproduction and reduce competition with the parent plant Key Terms seed a fertilized ovule, containing an embryonic plant · In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds Asexual Reproduction in Plants Asexual reproduction occurs through Vegetative Propagation, Budding, Fragmentation and;



Vegetative And Seed Reproduction Of Plants Tubers Bulbs And Seeds Stock Vector Illustration Of Vector Generative


Biology For Kids Flowering Plants
· Reproduction of plants Plants Non Flowering flowering By Flowers & Vegetative Spores Cones Seeds reproduction formation 3 Plant Asexual Reproduction Above ground Stems arch over and take root at the tips, forming new plants (Forsythia, Raspberry and Strawberry) Horizontal above ground stems are called stolons1700 · Stamens The male parts of the flower (each consists of an anther held up on a filament) Anthers Produce male sex cells (pollen grains) Stigma The top of the female part ofProducing plants from seeds has many advantages seen from the enduser's point of view, it produces many plants in each pot and the plants tend to be compact But more important is the fact that plants produced in this way grow on the same mineral wool from the time the seeds are put onto it to the time the plants leave the nursery



Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests



Science Plant Reproduction Without Seed English Youtube
Well, plants reproduce by several methods They Reproduction in PlantsSeed plants appeared about one million years ago, during the Carboniferous period Two major innovations—seed and pollen—allowed seed plants to reproduce in the absence of water The gametophytes of seed plants shrank, while the sporophytes became prominent structures and the diploid stage became the longest phase of the lifecycleApril 6, 21 How to deliver more seamless sales and marketing presentations virtually



There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express



Plant Reproduction Organismal Biology
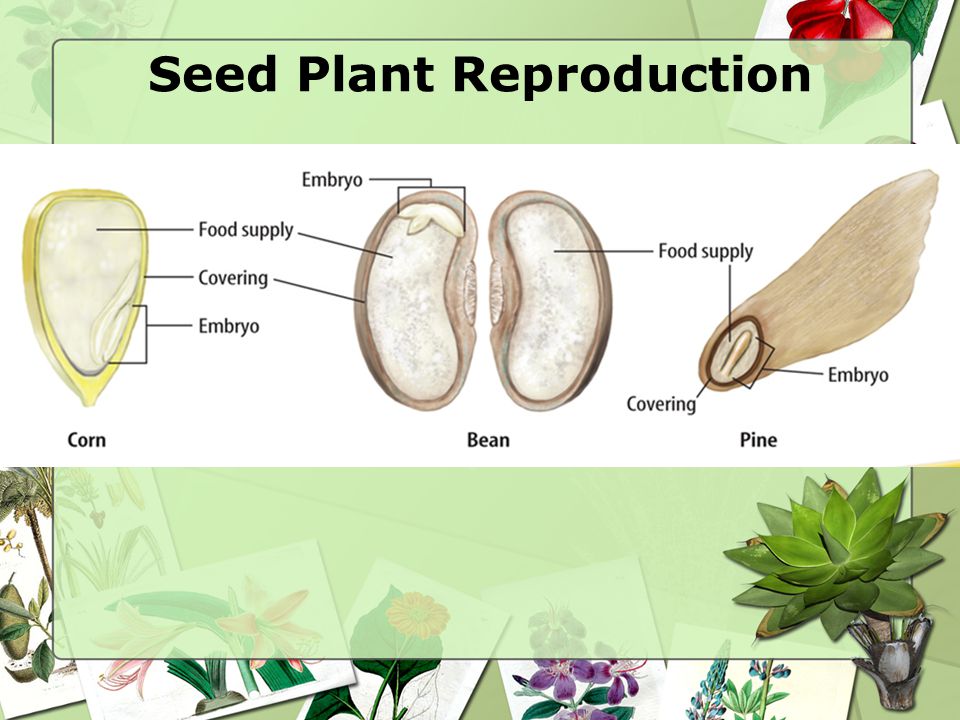
· PARTS OF A SEED A seed has 3 parts 1) Seed coat A cover that protects the seed 2) Embryo The baby plant 3) Stored food Seed coat Stored food Embryo 6 WE CAN CLASSIFY THE SEEDS ACCORDING TO Seed structure Water melons have flat small seeds Mangos and peaches have one seed Coconuts are giant seeds Where are seeds stored Flowers that bear "make" seeds like Apple trees Seeds · Almost all plants reproduce by sexually formed seeds, but they often complement reproduction by seed with clonal (asexual) reproduction, most often by stolons, rhizomes or similar organs capable of rooting and/or resprouting and forming new fully functional individuals (Mogie & Hutchings 1990;Reproduction in Plants G7 7 Videos 0026 Hours Share All organisms increase their numbers by adding new individuals in their population The process of giving birth to same species of living organisms is called "Reproduction" Ever wondered how plants reproduce?


Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S


Plant Reproduction Biology Junction
Or what methods do they adopt for reproduction? · Evolution of Seed Plants The lush palms on tropical shorelines do not depend upon water for the dispersal of their pollen, fertilization, or the survival of the zygote, unlike mosses, liverworts, and ferns of the terrain Seed plants, such as palms, have broken free from the need to rely on water for their reproductive needs · Seed plants mainly multiply by seeds Seedless plants multiply by spores that may produced asexually or as a consequence of asexual reproduction Krishan T · 2 · Jan 24 15



Plant Classification Reproduction Plants Can Be Classified Into 2 Main Groups Non Seed Plants Mosses No Vascular Systems Ferns Vascular Systems Ppt Download


Reproduction In Plants
Well, plants reproduce by several methods They can be asexual as well as sexual To our surprise, there is an additional method of reproduction called "Vegetative Reproduction" in plantsModes Of Reproduction In Plants In plants, reproduction is carried out via two modes Asexual Mode – New plants are obtained without producing seedsThe seed is the reproduction method of plants that produce seeds The seed is an incredible biological feat, containing everything required to produce


Part 3 Growth Reproduction And Evolution Plant Reproduction Aceites Esenciales Dōterra



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub



1 Seed Formation Sexual Reproduction In Plants



Learn Characteristics Of Living Organisms Nutrition Growth Reproduction And Lifespan In 3 Minutes



Plants Without Seeds Plant Reproduction Dk Find Out


Sexual Reproduction Grade 11 University Biology


Flowering Plant Reproduction



Reproduction Without Seeds By Hanisha Brar



Flowering Plants Reproduction Worksheet
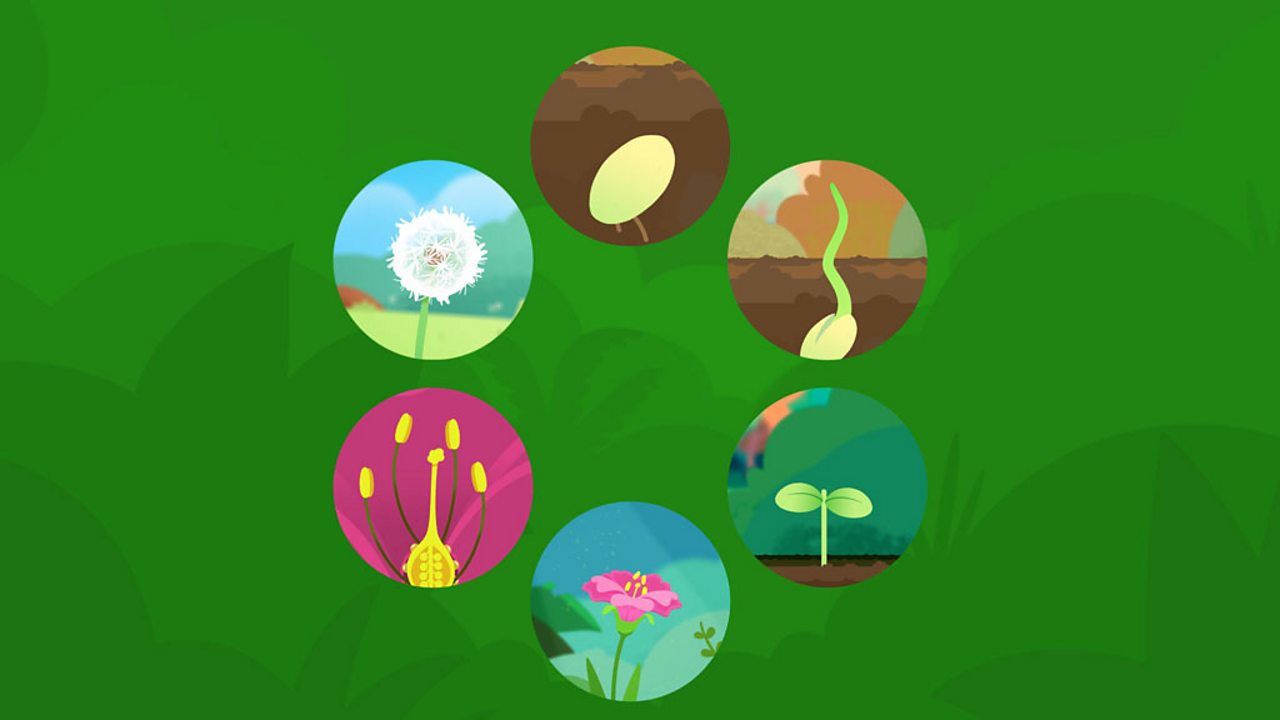



What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub


Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S



Fern Reproduction Seed Less Vascular Plants Diagram Quizlet


The Seed Biology Place Seed Evolution



Plant Reproduction Plants



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants


Sexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online



Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help



Plant Sexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids Youtube



Reproduction System Reproduction Systems In Plants Seed Propagated


Plant Reproduction Organismal Biology



Reproduction Of Flowering Plants Zainab Waheed



Ppt Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



How Do Seed Plants Grow Reproduce



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii



Plant Reproduction



Plant Reproduction Powerpoint Presentation Lesson Plan Powerpoint Lesson Plans Alternation Of Generations Powerpoint Lesson



Plant Reproduction Bioninja


Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science


Plant Reproductive Development And Structure Boundless Biology


How Do Plants Reproduce Sexually B4fa
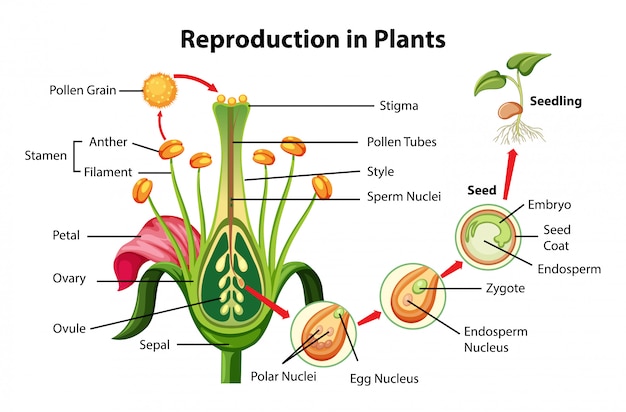


Free Vector Reproduction In Plants Diagram



Outdoor Education School Science Camps California



Seeds And Flowers Plant Reproduction Plants Without Seeds



Seed Plant Evolution Ck 12 Foundation


How Seep Plants Reproduce Study Sheet Hanford Christian School Jane Kitson



Plant Reproduction Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Class 5th Science Reproduction In Plants Chapter 1 Youtube
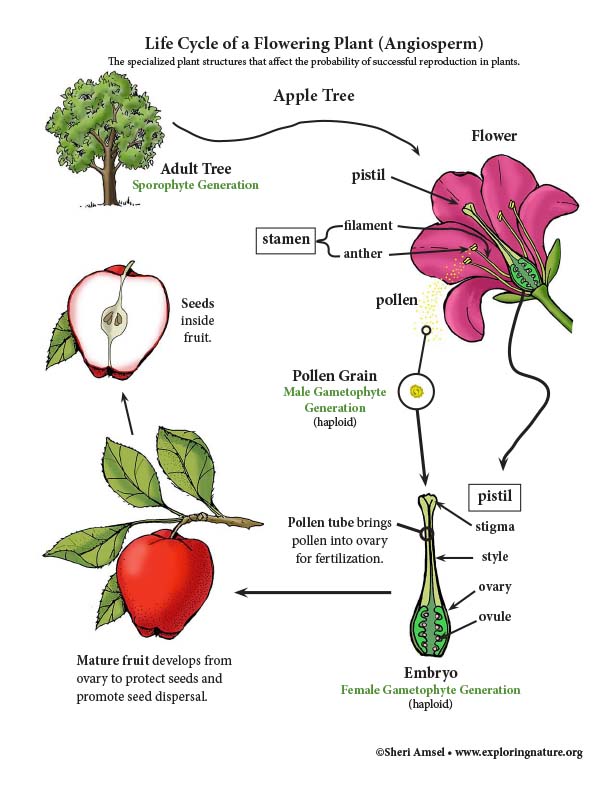


Plant Reproduction Illustrated Growth And Development Of Organisms Ngss 6 8 Grade



Plant Reproductive System Angiosperms Britannica
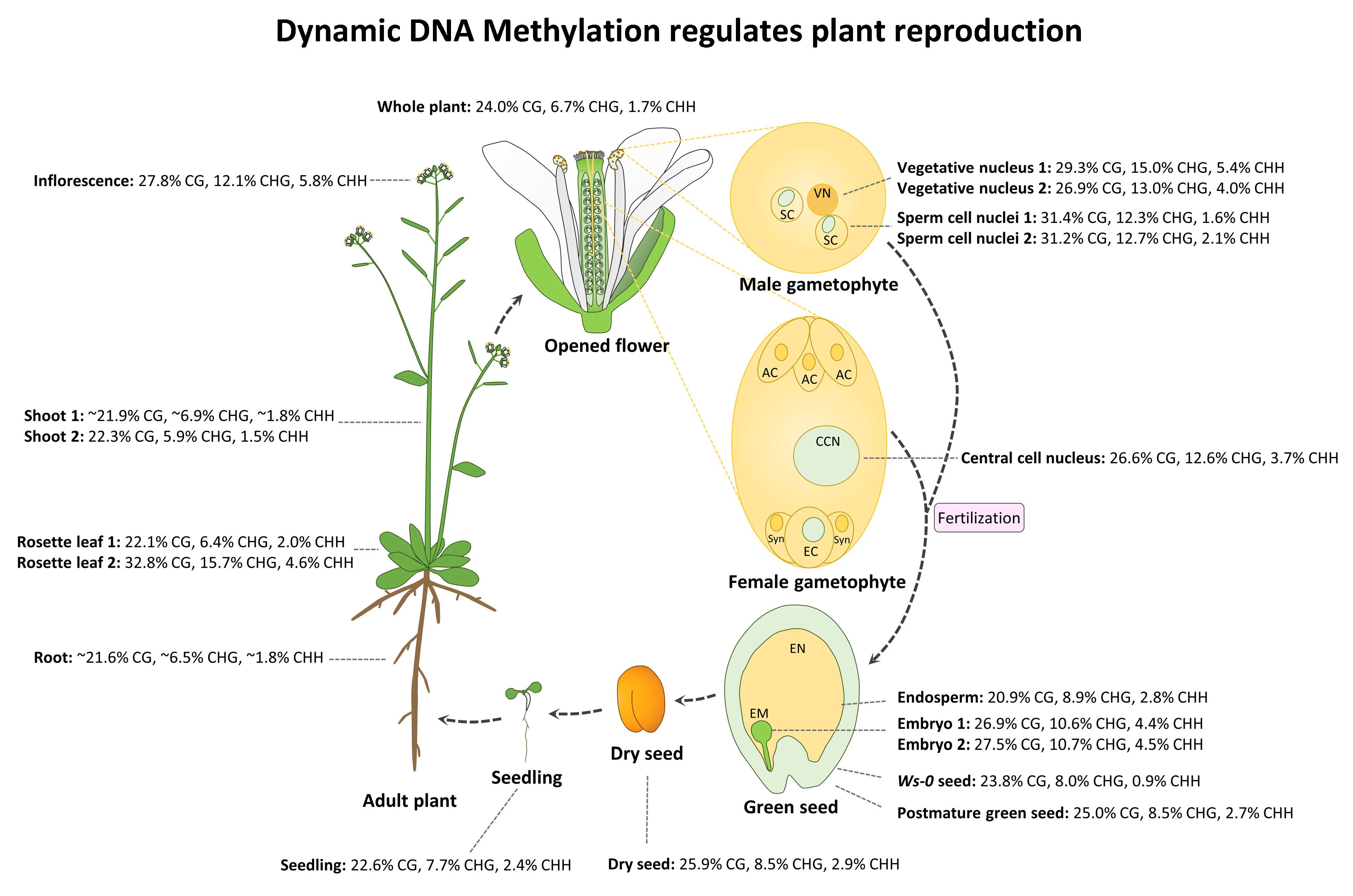


Plants Free Full Text Epigenetics Regulates Reproductive Development In Plants
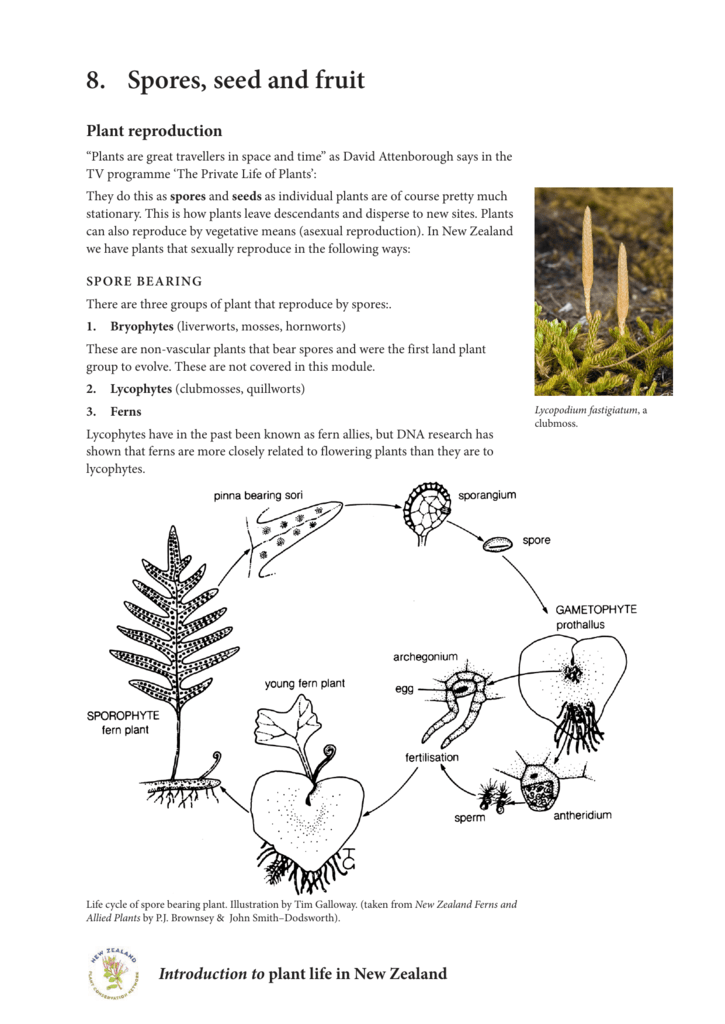


8 Spores Seed And Fruit New Zealand Plant Conservation Network


3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download


Plant Reproduction Seeds And Spores Cut And Paste Activity By King Virtue



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants



Reach For The Sun Lesson 3 Plant Life Cycles And Reproduction Filament Games



Ovary Botany Definition Structure Britannica


Ncert Class 7 Science Twelfth Chapter Reproduction In Plants Exercise Solutions


Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs


Plants Reproduction Stock Illustrations 253 Plants Reproduction Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



5 Reproduction Of Plants How Do Plants Reproduce



Lesson Worksheet Sexual Reproduction In Plants Nagwa
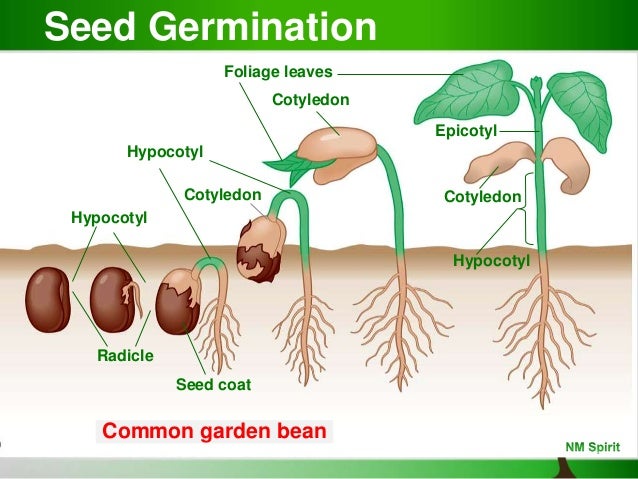


Plant Reproduction Development



Plant Reproduction The Biology Primer



Plant Reproduction 9 4 Plants Can Reproduce In


Life Cycle Of A Plant



Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S



13 3 Sexual Reproduction In Seed Plants



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub



How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow



Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica



Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica


Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant



Plant Reproduction Bioninja
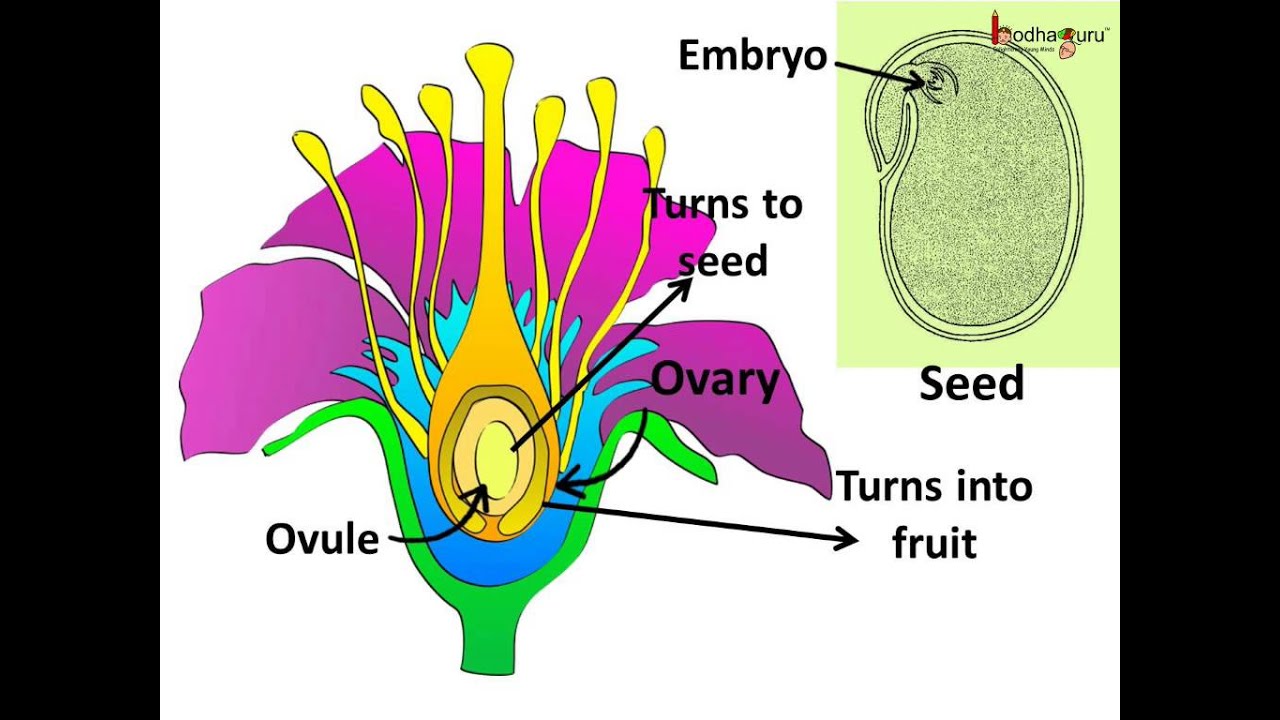


Science Sexual Reproduction In Plants Pollination Fertilization Hindi Youtube


Flowering Plant Reproduction



Plant Reproduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
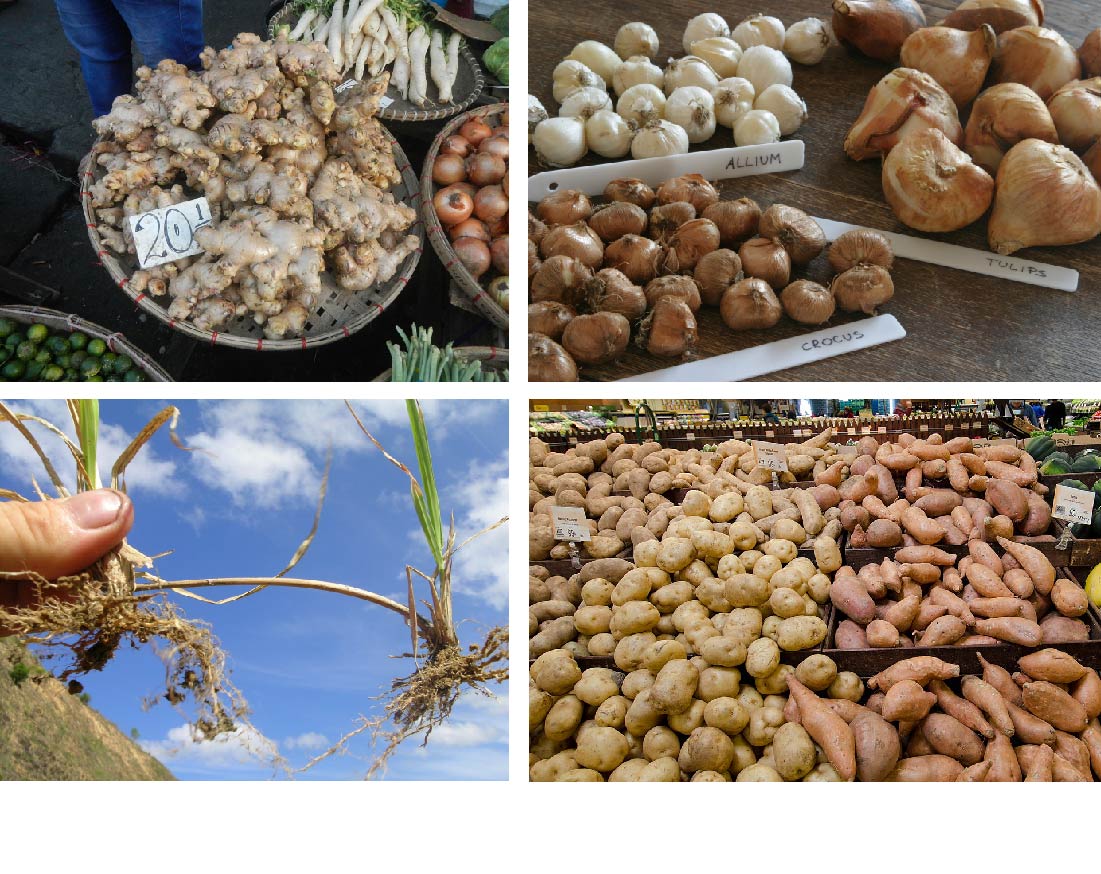



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science
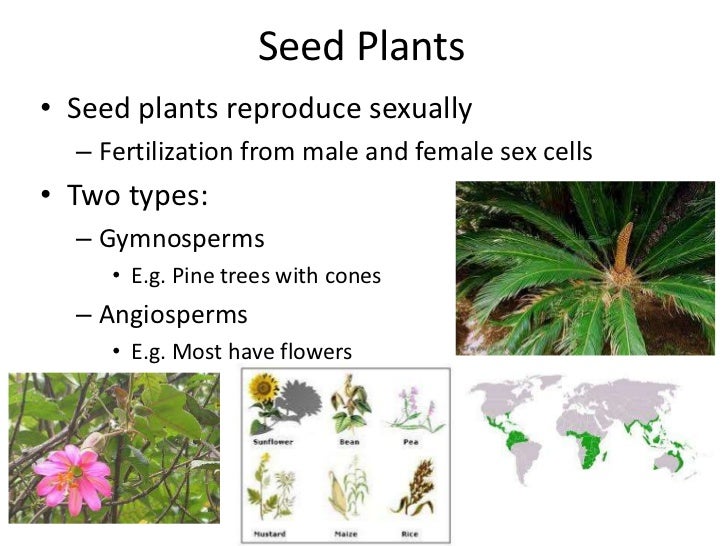


Plant Reproduction Seed Plants


Flowering Plant Reproduction



How Does The Reproduction Of Seedless Plants Differ From That Of Seed Plants The Millennial Mirror



How To Grow From Seed The Garden Of Eaden



Pin On Fruit Seeds


Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii
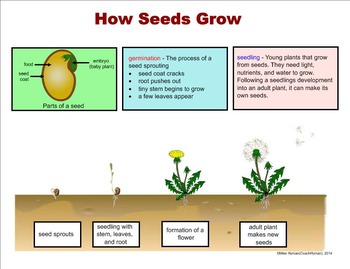


Seed Plant Reproduction A Fourth Grade Smartboard Introduction By Mike Hyman


Plant Growth And Reproduction The Biology Of Sex And Death Bio 12



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿